Storage of cryptocurrency can be described broadly as two kinds of wallets which include hot wallets and cold wallets. Both these play crucial roles in the safety of digital assets but are starkly differentiated by their approach on matters of security, convenience, and functionality. The decision on the wallet depends upon what you require it for, the amount of transactions, and what level of security is required. Let’s go into hot wallet vs cold wallet, how these wallets work, what advantages they might have, drawbacks, and how to choose one that fits best according to your needs.
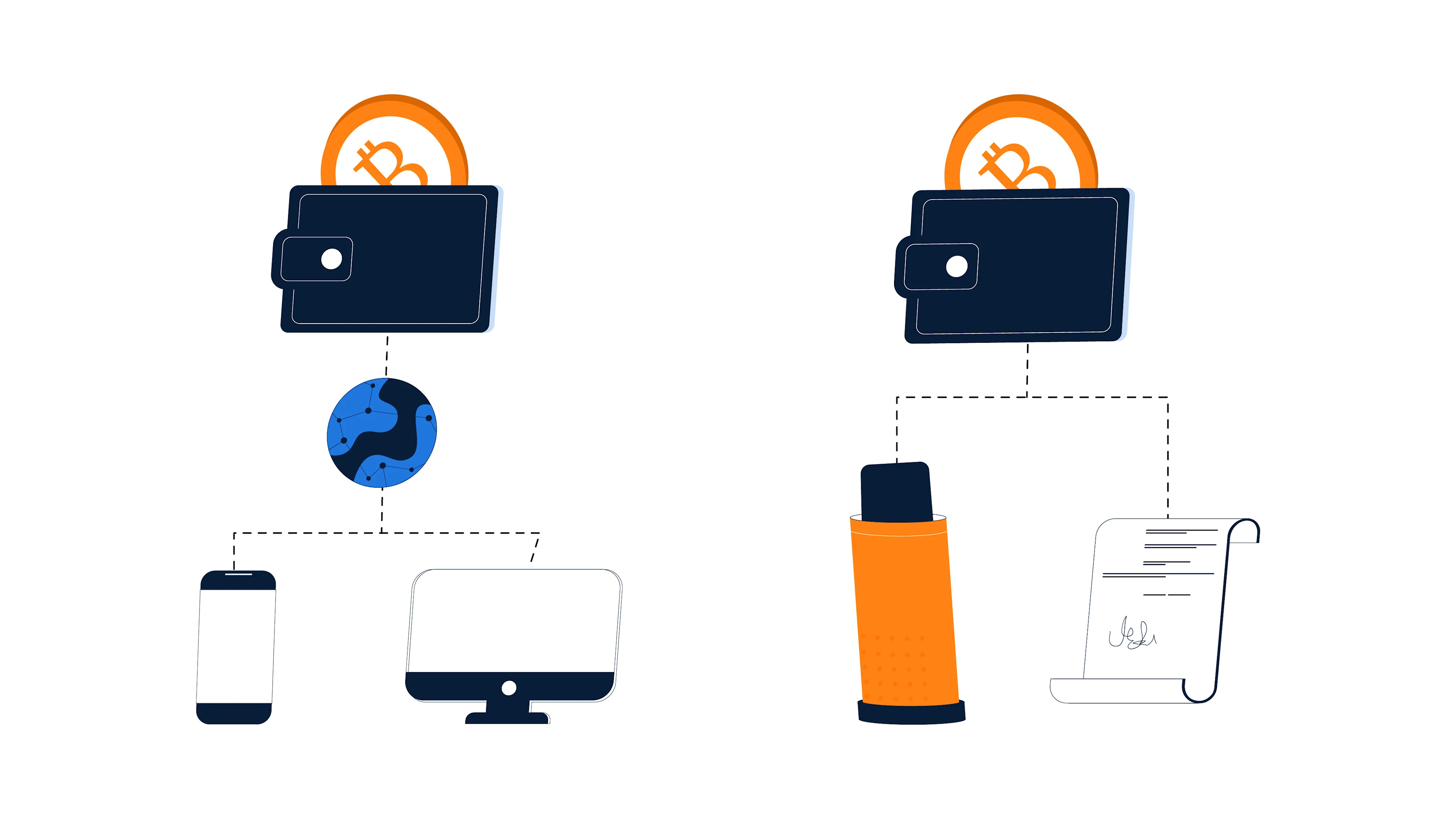
What Is a Hot Wallet?
A hot wallet, also known as software wallet, refers to an internet-connected digital wallet. Generally, a hot wallet appears as apps or software you install on devices like your phone, tablet, or computer. It is very convenient for frequent transactions because your funds are always available to you. However, with this convenience comes a trade-off regarding security.
Key Characteristics of Hot Wallets
- Online Seed Generation: It is generated and kept online in a hot wallet. The seed phrase will be unique words in and by themselves to recover your wallet. However, since it is generated online, the seed phrase has the chances of being exposed to cyber attacks.
- Digital Storage of Private Keys: Private keys with a hot wallet are stored online. A password is the protection of your wallet; however, an internet-linked device exposes your private keys to danger via hacking and cyber attacks.
Advantages of Hot Wallets
- Convenience: Hot wallets are user-friendly, easy to set up, and easy to access. Hot wallets are great for beginners and an active trader who needs fast and rapid access to his funds.
- Ease of transactions: Hot wallets have streamlined the whole process associated with buying, selling, and transferring cryptocurrency. For that reason, most users of Web3 applications would interact with decentralized apps (dApps) and smart contracts using hot wallets.
- Accessibility: With the wallets being online, you can access them from anywhere around the globe provided you have an internet connection.
Drawbacks of Hot Wallets
- Security Risks: Because wallets are online, the risk of hot wallets being hacked, phishing, or malware access exists.
- Less security for high-value assets: Hot wallets are probably not secure enough for larger holdings since private keys always stand to be compromised.
Best Use Case: Hot wallets are good for everyday transactions and experiments in web3 applications. However, not ideal for storing large values, as it might compromise security.
What Is a Cold Wallet?
A cold wallet is an offline wallet used to store cryptocurrency. Cold wallets are generally more secure as they do not connect to the internet. In contrast to hot wallets, the chance of online attacks is much reduced in cold wallets. Therefore, they tend to be ideal for long-term storage, often called “cold storage.” Usually, hardware devices such as Ledger or Trezor form cold wallets, though others may be paper wallets or sound wallets.
Key Characteristics of Cold Wallets
- Offline Seed Generation: With a cold wallet, keys to private accounts are generated and stored offline. It ensures that no third party can reach your seed or private keys in the offline system.
- No Internet Connection: When it comes to traditional storage, they do not necessarily need a connection to the internet. Such an “air-gapped” approach will certainly keep your private keys together with the other sensitive data isolated from potential digital threats.
Advantages of Cold Wallets
- Increased Security: Cold wallets cannot be hacked as they are offline, malware, and phishing.
- Protecting High Value Assets: Mainly, cold wallets are used by those who do everything possible to keep their assets as safe as possible, especially those holding large amounts of crypto.
- Reduced Exposure of Risks on Smart Contracts: A cold wallet does not interact directly with any smart contract. Hence, the risk due to interaction with malicious contracts will be avoided, and it should be used more for storing than for any transaction purposes.
Drawbacks of Cold Wallets
- Less Convenient: Cold wallet requires a much more complex process than the hot wallets, in order to access the funds; therefore, less ideal for frequent transactions.
- Initial Cost: The most common type of cold wallet is hardware wallet; they essentially demand an upfront investment, which may be unappealing to a majority of the users.
Best Use Case: Those holding large amounts of cryptocurrency who do not regularly need access to their funds should be stored in cold wallets.
Hot Wallet vs Cold Wallet: Which Should You Choose?
The choice between the hot wallet vs cold wallet largely depends on your planned usage of cryptocurrency. If you are a high-frequency transactor-that is, someone who frequently buys, sells, or engages with Web3 applications-a hot wallet would be the best option due to its handy availability and convenience in handling daily transactions that involve a great need for quick access to funds.
On the other hand, a long-term holder who treats his cryptocurrency as an investment and is less likely to do numerous transactions may actually get much more value from a cold wallet. Cold wallets have better security while off-line, so it is better suited to hold large holdings in case online attacks become the problem.
Most of the users find the hybrid approach effective, ensuring maximum convenience and security at all times. Perhaps they have a hot wallet available for daily transactions but keep a cold wallet in reserve as a “vault” to store more significant sums. Hardware devices, such as Ledger, can even host multiple wallets on the same device, allowing you to create one for most of your Web3 interactions, for example, while storing your large balances in cold storage. That makes for a balanced solution: accessible on a daily basis, but big balances safely kept offline.
SEE ALSO: Historical Shiba Inu Coin Price Trends: What Can Beginners Learn?
Setting Up a Secure Wallet System
If you do decide to take the hybrid approach, here are the steps you need to set up a secure and organized wallet system:
- Establish Separate Wallets for Each Purpose: Set up two separate wallets on a Ledger type of device – one cold wallet as an actual safe with which you are going to conduct transactions and a hot wallet purely designed for online transactions.
- Store Most of Your Assets in Cold Storage: Put most of your crypto funds into your cold wallet. Your cold wallet will not interact with smart contracts or Web3 applications.
- Limit Transfers to the Hot Wallet: Transfer only small amounts to your hot wallet based on necessity. This will keep minimal exposure and large holdings safe.
Conclusion: Hot Wallet vs Cold Wallet
The decision between hot wallet vs cold wallet need not be all-or-nothing. Each one has its strengths and ideal use case, to allow the user to meld them harmoniously. For active users who care about access, there will always be an at-your-fingertips solution in a hot wallet. For more security-conscious users-those who might want to hold it for a long time, a cold wallet can be rather comforting. You’ll be able to enjoy the best of both worlds: accessibility for day-to-day transactions and top-level security for the majority of your assets.
In this rapidly evolving landscape of digital assets, the power to manage one’s security ultimately lies in your hands. Embrace the strengths of hot and cold wallets with a flexible, secure approach to managing cryptocurrency holdings.



