Satoshi Nakamoto developed Bitcoin in 2009 as a decentralized digital money. It has become the most popular cryptocurrency, revolutionizing the concept of money. It’s the first cryptocurrency and the most popular; therefore, new users should learn how it works. Understanding Bitcoin operations helps people navigate this complex digital environment. Bitcoin trades use blockchain technology. This safe, open, and immutable ledger records all transactions. Understanding blockchain helps new users appreciate Bitcoin’s safety and usefulness. This will help individuals make sensible digital currency decisions.
Basics of Bitcoin Transactions
Bitcoin transactions transfer money between Bitcoin wallet. A transaction must specify how much Bitcoin is being sent and to whom to send Bitcoin.
Bitcoin transactions consist of inputs, outputs, and the transaction value. The individual sending Bitcoin must verify that they possess it using inputs, which are past acts. The sender’s address and Bitcoin amount are outputs. No money is transferred between wallets—just the transaction amount.
Bitcoin security requires public and private keys. A public key is like an address—anyone may transfer Bitcoin to a wallet. The private key is a secret code that allows the switch. Someone signs a trade with their private key. The unique digital signature reveals who owns the transaction and that it hasn’t changed. This method is secure because the private key is needed to fake a transaction. These aspects of the exchange procedure provide safety and clarity.
SEE ALSO: Bitcoin Wallets Explained: How to Set Up a Secure Bitcoin Wallet
How Blockchain Secures Bitcoin Transactions
1. Explanation of Blockchain as a public ledger
Blockchain technology, a public log, secures Bitcoin transactions differently. This ensures everyone can see deal records. Openness increases trust since everything is recorded and verifiable.
2. Blocks of data chained together to prevent tampering
Blockchains organize deals into blocks and link them in order. Each block carries a unique hash of the previous block. This is immediately apparent if someone changes data in one block. Changing one block in this chaining mechanism requires changing all the blocks following it, which is almost impossible.
3. Decentralized nature of Bitcoin: No single point of control
Independent, Bitcoin is not run from one place. Instead of one authority, numerous nodes run the network. The network is safer since thieves must take over most of it to modify transaction data. This makes fraud and other online hazards challenging to pass. All these reasons make Blockchain a solid basis for secure Bitcoin transactions.
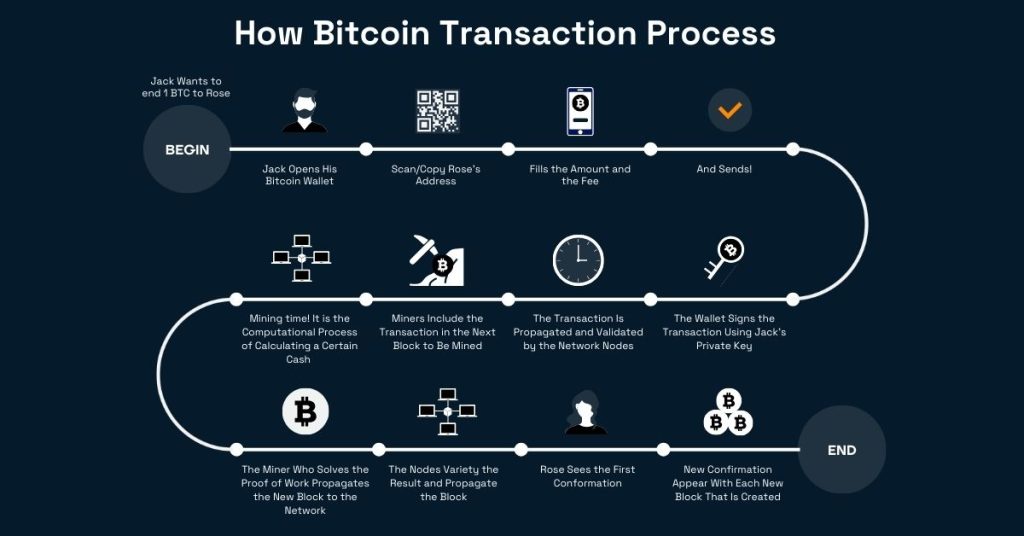
Step-by-Step Process of a Bitcoin Transaction
1. Creating a Bitcoin Wallet
Start using Bitcoin mining by creating a wallet. Keep your public and private keys here. Web, software, and hardware wallets are available. People can locate your public key address. Only you know your private key, which enables you to approve movements. Keeping this key safe is crucial since losing it prevents Bitcoin access.
2. Initiating the Transaction
Trading begins when your money is ready. Send money to someone by entering their Bitcoin address or public key. Check the address to avoid sending money to the wrong person. Next, enter the swap amount and, if desired, a charge. Mining companies are more likely to accept your deal with fees. Work usually moves faster when fees are more significant.
3. Broadcasting to the Network
The Bitcoin network receives the Bitcoin transactions data. Bitcoin nodes—computers that store the Blockchain—receive the transaction. They verify the trade’s legitimacy by verifying the person’s funds and network rules. Next, avoid using the same Bitcoin for several transactions. This prevents double-spending.
4. Mining and Block Confirmation
The mining procedure begins after transaction verification. This is a race amongst miners to add blockchain blocks, which retain unfinished trades. A miner adds your transaction to the Blockchain as a block after solving a complex math problem. Always get six confirmations before finalizing a contract. It will ease your mind. Each confirmation makes a transaction on the Blockchain harder to modify since it increases its likelihood of being honest. This multi-step method makes Bitcoin payments secure, fast, and straightforward.
Transaction Fees and How They Are Determined
The ranking of Bitcoin transactions depends on transaction fees. Users can set a charge to encourage miners to start trading faster. When costs are high, especially when the network is congested, discoveries are faster.
Several factors affect trading fees, including deal size and frequency. Block rooms become more popular when several users transfer Bitcoin simultaneously, raising costs. Bigger deals require more information, which makes,g fees more significant.
Many tools and websites may assist users in choosing the proper price. These evaluate the network’s current setup and offer advice based on trading trends and typical fees.
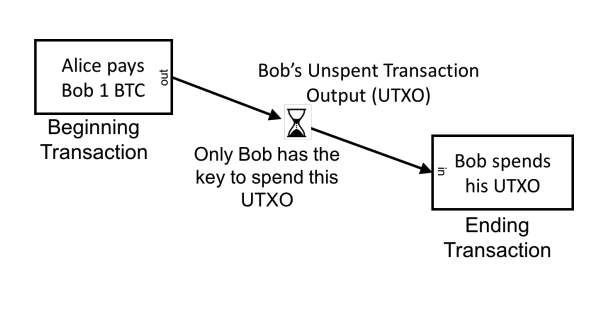
UTXO Model: The Foundation of Bitcoin Transactions
The Unspent Transaction Output (UTXO) technique is crucial to Bitcoin. UTXOs are unspent Bitcoin. Not so with accounts that maintain a fixed amount for each user. Every transaction uses UTXOs and creates new ones.
This method improves privacy and safety by making each contract unique. You can notice the money’s improvement. Bitcoin owners have more control since they may choose which UTXOs to pay. You also have more transaction number flexibility. This structure makes verification faster because nodes simply need to check UTXO availability. This speeds up transactions and secures the network.
SEE ALSO: Bitcoin Mining for Beginners: Can You Still Mine Bitcoin?
Common Issues and How to Avoid Them
The repeated digital currency spending troubles blockchain. Blockchain utilizes proof of work or proof of stake to verify transactions and prevent their removal from the chain.
If consumers lose their private keys, they may never regain access to their digital possessions. Encrypting files or storing money in hardware wallets are safeguards.
Unapproved transactions take time. Networks and miners verify transactions. Setting the proper transaction fees speeds up the process and prevents delays and cancellations. Understanding these challenges allows users to use blockchain technology safely and effectively.
Conclusion
Decentralized and peer-to-peer Bitcoin trade is unique. Cryptography and miner agreements secure transactions and this writing style reduces scams. Bitcoin’s growing role in global banking allows for new ideas. Bitcoin might make international money transfers more accessible and increase money access. Blockchain is helpful beyond cash. Safe and transparent deals might affect several industries. Bitcoin and Blockchain will transform global banking when new laws are implemented, and more people utilize them.
FAQ
How long does a Bitcoin transaction take to confirm?
If the network can’t create a disturbance, then Bitcoin transactions take only 10 minutes. Transaction costs affect confirmation speed.
Why do Bitcoin transactions have fees?
Bitcoin miners must be compensated to process transactions. In busy networks, more fees can speed things up.
What happens if I send Bitcoin to the wrong address?
You can’t recover it, so do it carefully.
How many confirmations are needed for a transaction to be secure?
Most Bitcoin transactions are secure after six confirmations. This ensures the network has adequate transaction evidence.
Can Bitcoin transactions be reversed?
No, Bitcoin transactions are irreversible. The fact that blockchain technology is unchangeable is crucial.



